|
Ankle sprains are a common but painful injury that can temporarily limit your mobility. Recent studies have shed light on the most effective treatments for managing this condition. A systematic umbrella review by Gaddi et al. (2022) in Frontiers in Medicine examined multiple studies to establish a clear guide for treating acute ankle sprains. Here’s what you need to know to navigate the recovery from an ankle sprain effectively.
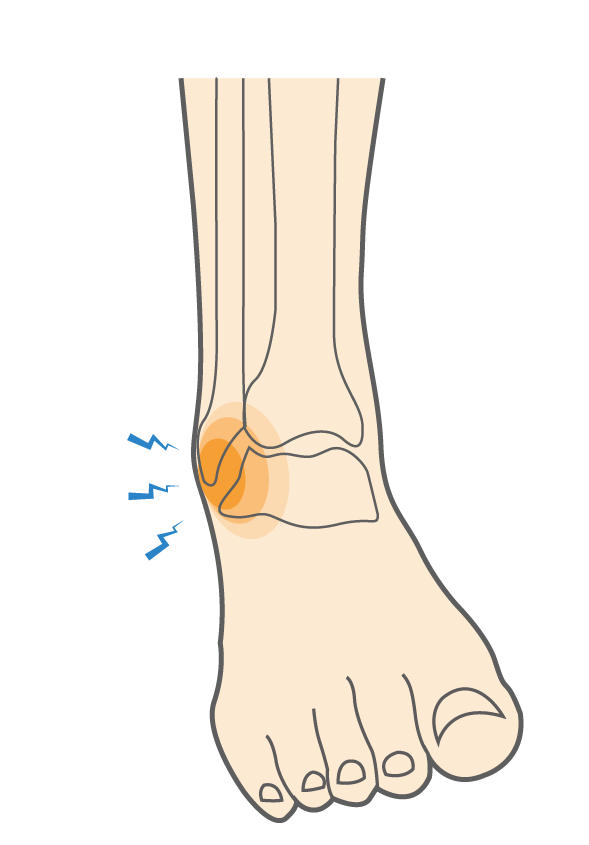
Understanding Ankle SprainsAnkle sprains occur when the ligaments that stabilise the ankle are overstretched or torn, usually due to twisting or rolling the foot. Symptoms typically include pain, swelling, and limited mobility. While these injuries are prevalent, especially in physically active individuals, understanding the latest research can significantly aid recovery. Effective Non-Surgical TreatmentAccording to Gaddi et al. (2022), non-surgical interventions are highly effective in managing acute ankle sprains. These treatments focus on minimising pain and swelling while optimising the healing process without the need for surgery. Here are the key findings:
ConclusionRecovering from an ankle sprain requires patience and adherence to proven treatment protocols. The insights from the umbrella review by Gaddi et al. (2022) emphasise the importance of functional recovery programs and appropriate pain management, tailored to individual needs and medical advice. By following these evidence-based recommendations, patients can expect a more efficient and effective recovery. References
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Author
Archives
May 2024
|
Copyright Acland Street Physiotherapy © 2024

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed