|
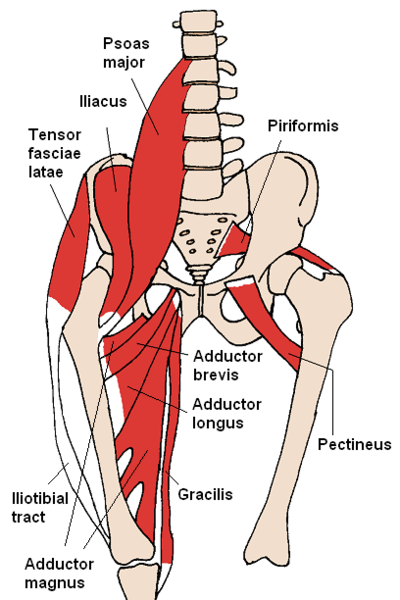
Groin strains or tendinopathies generally occur with sports such as martial arts, football or ice hockey. The muscle belly-tendon part of the adductor tendon or where this tendon inserts to the pubic (hip) bone is generally tender when pressure is placed on it. The adductor longus muscle is the most commonly injured. Common risk factors to increasing the risk of injury the groin muscles include a weakness in adductor muscles and a core muscle weakness (tranversus abdominals).
The key differences between groin strains and tendinopathies are notably:
These injuries can respond very well to physiotherapy management which may include dry needling, manual therapy, extracorporeal shockwave, core stability, stretching and eccentric strengthening rehabilitation programs. Note for that groin related tendon injuries, exercise rehabilitation can take 3-6 weeks before full recovery can occur.
0 Comments
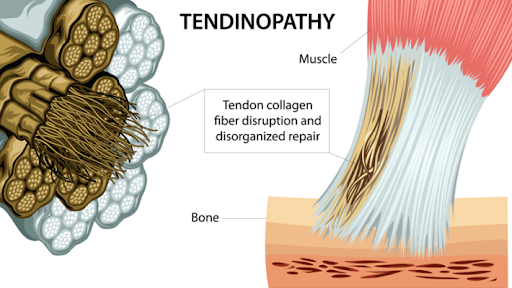
Tendinopathy is a generic term used to describe injuries to the tendon associated with inflammation and degeneration. It can be either characterised as a painful or pathological condition associated with overuse. Usually pain is associated with increased loads and a recognition that there has been a relative increase in inactivity. Pain is often reported as sharp early on and then becomes a dull ache weeks later. Pain may be present at the beginning of the activity then disappear during it, then returns on subsequent attempts of the activity.
Tendinopathies are common as they have a poor blood or nutrient supply compared to skeletal muscles. In fact, the oxygen consumption of tendons is about 7.5 times lower than skeletal muscles. A relatively low metabolic rate results in generally slow healing after injury. Common tendinopathies seen at Acland Street Physiotherapy include:
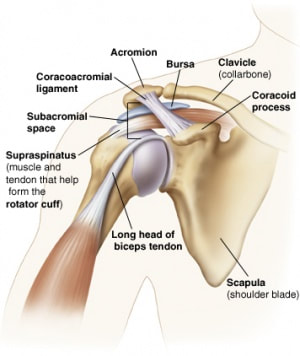
Tendinopathies generally respond well to physiotherapy treatment. This could include treatment techniques such as manual therapy, extracorporeal shockwave and eccentric strengthening exercises to improve the load capabilities of the tendon. Subacromial pain syndrome is a non-traumatic one sided condition of the shoulder. This common condition is two thirds of all shoulder complaints at Acland Street Physiotherapy. This condition is more prevalent as you age. It usually causes pain localised around the acromion (bony process of the shoulder) when lifting the arm. Usually one or structures are injured within the subacromial space.
Common conditions that cause subacromial pain syndrome include:
The above conditions often respond very well to physiotherapy treatment which includes manual therapy, dry needling, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, exercise programs involving stretching, strengthening the rotator cuff and stabilising the scapula (shoulder blades). |
Author
Archives
May 2024
|
Copyright Acland Street Physiotherapy © 2024

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed