|
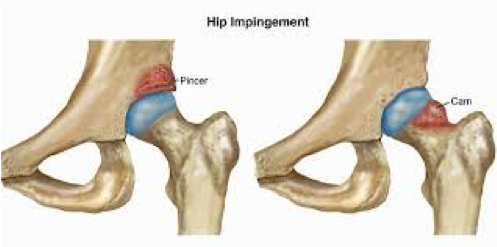
Femoral acetabular impingement or "hip impingement" is a condition which involves abnormal contact of the hip joint between the ball of the hip and socket of the pelvis. The cause is generally multi-factorial which include childhood hip issues and repetitive strain or hip rotation. Clinical signs and imaging can confirm this diagnosis accurately. Patients often report pain and stiffness in the hip or groin area. Symptoms are often aggravated by squatting, climbing upstairs and prolonged sitting. This condition can respond well to physiotherapy treatment which may include manual treatment, strengthening and neuromuscular exercises. Surgery is often indicated as well as post surgical physiotherapy rehabilitation.
1 Comment
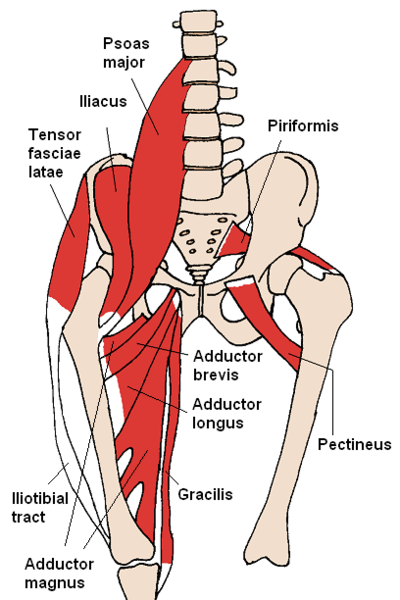
Groin strains or tendinopathies generally occur with sports such as martial arts, football or ice hockey. The muscle belly-tendon part of the adductor tendon or where this tendon inserts to the pubic (hip) bone is generally tender when pressure is placed on it. The adductor longus muscle is the most commonly injured. Common risk factors to increasing the risk of injury the groin muscles include a weakness in adductor muscles and a core muscle weakness (tranversus abdominals).
The key differences between groin strains and tendinopathies are notably:
These injuries can respond very well to physiotherapy management which may include dry needling, manual therapy, extracorporeal shockwave, core stability, stretching and eccentric strengthening rehabilitation programs. Note for that groin related tendon injuries, exercise rehabilitation can take 3-6 weeks before full recovery can occur. |
Author
Archives
May 2024
|
Copyright Acland Street Physiotherapy © 2024

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed